What is DevOps...Its Benefits and Automation, Scaling, Infrastructure in DevOps.
DevOps is a methodology that combines software development and IT operations into a single process. It involves automating the entire software delivery process, from code creation to testing, deployment, and monitoring. DevOps is not just a tool or a technology, but rather a culture that promotes collaboration and communication between developers and operations teams.
Benefits of DevOps
DevOps has numerous benefits, some of which are:
Faster time-to-market: DevOps practices enable teams to deliver software faster by automating manual tasks, such as testing and deployment.
Improved quality: Automated testing and continuous monitoring ensure that software is of high quality and meets user requirements.
Greater efficiency: DevOps practices eliminate manual tasks and reduce the risk of errors, resulting in greater efficiency.
Better collaboration: DevOps brings together developers and operations teams, which promotes better collaboration and communication.
Increased agility: DevOps enables teams to respond quickly to changes in user requirements or market conditions.
Automation in DevOps

Automation is a critical component of DevOps. It involves automating the entire software delivery process, from code creation to testing, deployment, and monitoring. Automation enables teams to eliminate manual tasks, reduce errors, and deliver software faster. Some examples of automation in DevOps include:
Continuous Integration (CI): CI involves automatically building and testing code changes as soon as they are committed to the code repository.
Continuous Delivery (CD): CD involves automatically deploying code changes to production as soon as they pass all tests.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): IaC involves using code to automate the creation and management of infrastructure, such as servers and networks.
Automated Testing: Automated testing involves using tools to automatically test software, reducing the risk of human error and improving quality.
Scaling in DevOps

Scaling is another critical component of DevOps. It involves designing and implementing systems that can handle increased load and traffic. Scaling enables teams to deliver software that can handle a high volume of users and traffic. Some examples of scaling in DevOps include:
Horizontal Scaling: Horizontal scaling involves adding more instances of an application or service to handle increased load.
Vertical Scaling: Vertical scaling involves increasing the resources, such as CPU and RAM, of a single instance of an application or service to handle increased load.
Load Balancing: Load balancing involves distributing traffic across multiple instances of an application or service to improve performance and handle increased load.
Infrastructure in DevOps
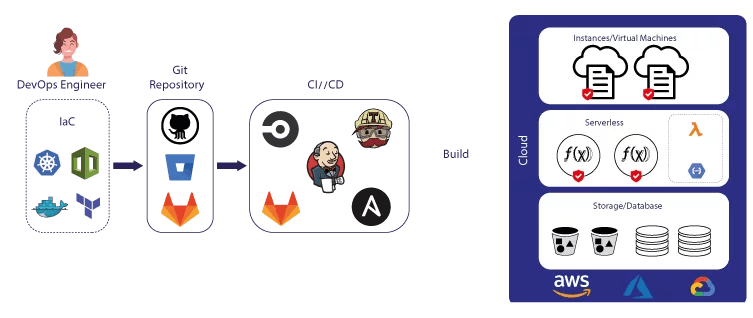
Infrastructure is a key component of DevOps. It involves designing and managing the hardware and software required to run applications and services. Infrastructure can be physical, such as servers and networks, or virtual, such as cloud-based servers and networks. Some examples of infrastructure in DevOps include:
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing involves using remote servers and networks to run applications and services, reducing the need for physical hardware and infrastructure.
Containers: Containers are lightweight, portable, and isolated environments that can run applications and services, simplifying deployment and management.
Configuration Management: Configuration management involves using tools to manage the configuration of infrastructure, such as servers and networks, ensuring consistency and reducing errors.
Conclusion
Automation, scaling, and infrastructure are critical components of DevOps that enable teams to deliver software faster, with better quality, and at scale. Automation involves automating the entire software delivery process, from code creation to testing, deployment, and monitoring. Scaling involves designing and implementing systems that can handle increased load and traffic. Infrastructure involves designing and managing the hardware and software required to run applications and services. By leveraging automation, scaling, and infrastructure, teams can deliver software that meets user requirements, at scale and with high quality.
~Puneet 🙃
